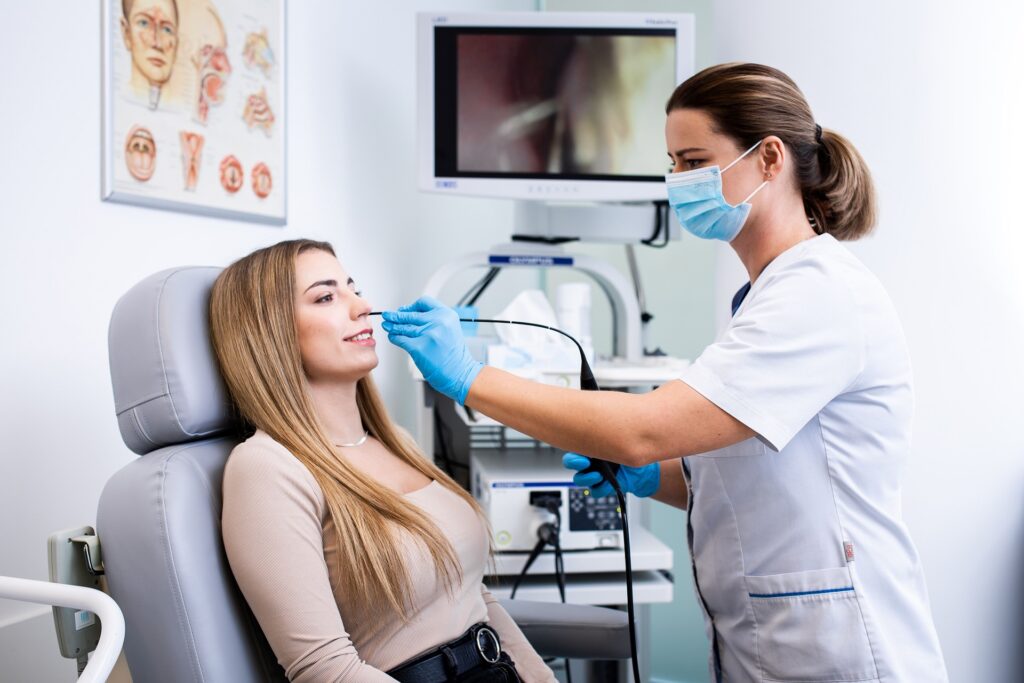
Fiberoptic examination is performed in a state of pharmacological sleep. Its purpose is to find a place of narrowing or obturation in the nose, throat and larynx in patients who suffer from snoring and sleep apnea. It is often used when previous diagnosis is uncertain and it is necessary to do precise tests to confirm the results.
The procedure starts by the anesthesiologist inducing the patient in pharmacological sleep by intravenously administering sedatives. During the procedure, a short fiberscope with a camera on top is put inside the nose. The camera allows precise assessment of narrower places in the respiratory tract and vibration of the tissues. At the same time, parameters such as blood oxidation, pulse and EKG are measured. Image from the camera is registered in order to discuss it with the patient during the next visit and suggest further treatment. One of the advantages of fiberoptic examination is the ability to record a video and take high-quality pictures imaging the upper respiratory tract during sleep, which allows replay and precise analysis and provides valuable diagnostic material.
It is sometimes possible to do a correction surgery in the same pharmacological sleep cycle, by eliminating the structure causing snoring or sleep apnea.